SQL aggregate functions AVG, COUNT, MAX, MIN, SUM are used the most. That is because we often need to add, make average or find the highest or lowest value.
It is mandatory to use GROUP BY clause anytime when we use aggregate function. (except for operations over windows using OVER())
List of SQL Server Aggregate Functions
AVG() – returns average value from the table
COUNT() – returns number of rows (values)
MAX() – returns maximal (highest) value
MIN() – returns minimal (lowest) value
SUM() – returns total of values
The combination of the aggregation function and the GROUP BY clause allows data to be aggregated (for example, in the GROUP BY article), this is important in order to reduce the atomicity of the data.
Example
Let’s have a table with Sales [SalesAmount] and date of order [OrderDate].
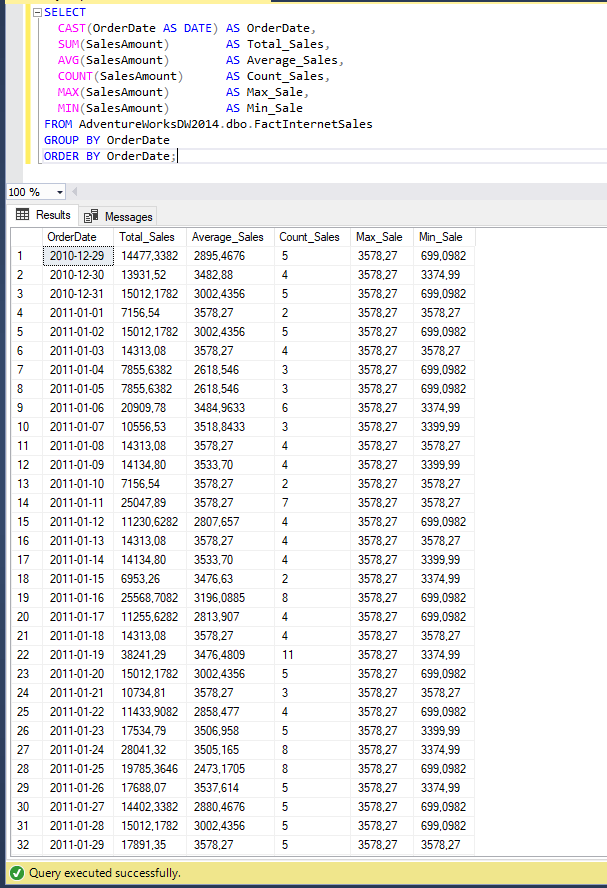
We will apply all aggregate functions on the sales column. It can be seen well on this example:
SELECT CAST(OrderDate AS DATE) AS OrderDate, SUM(SalesAmount) AS Total_Sales, AVG(SalesAmount) AS Average_Sales, COUNT(SalesAmount) AS Count_Sales, MAX(SalesAmount) AS Max_Sale, MIN(SalesAmount) AS Min_SaleFROM AdventureWorksDW2014.dbo.FactInternetSalesGROUP BY OrderDateORDER BY OrderDate;