UNION operator makes it possible to connect 2 results of query and remove all existing duplicities in them. In other words, operator actually performs DISTINCT (like SELECT DISTINCT) in final unification of records.
SQL UNION Syntax
SELECT Column FROM dbo.Table WHERE Condition
UNION
SELECT ColumnFROM dbo.TableWHERE Condition;
Syntax is same as in all Set operators. Result of unification is all records from both tables – If there is a column (or columns) with identical value in both tables, only unique value will be the result. UNION Operator performs unification and removes duplicities
SQL UNION Example
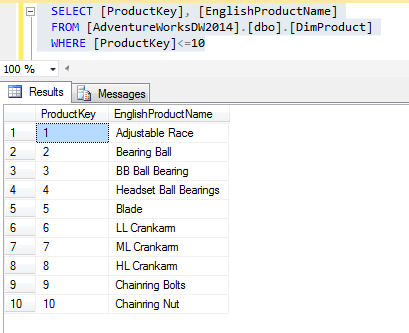
Let’s have a table with a list of products
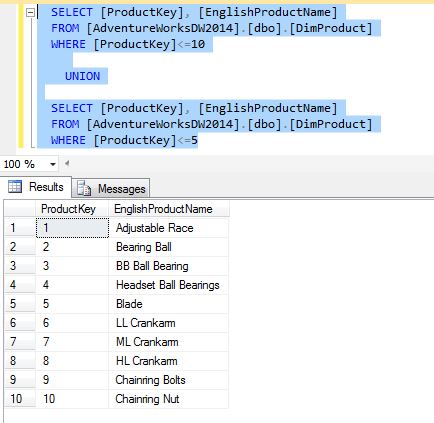
We will perform unification of 2 queries to demonstrate my point:
- first query – records where Product Key (Primary key) is lower than 10
- second query – records where Product Key (Primary key) is lower than 5
Script:
SELECT [ProductKey], [EnglishProductName] FROM [AdventureWorksDW2014].[dbo].[DimProduct] WHERE [ProductKey]<=10
UNION
SELECT [ProductKey], [EnglishProductName] FROM [AdventureWorksDW2014].[dbo].[DimProduct] WHERE [ProductKey]<=5;
Script result: