From time to time, it’s important to examine the database objects in terms of table size (number of rows and storage) to avoid some performance issues on server.
How to Check Table Sizes in a SQL Database
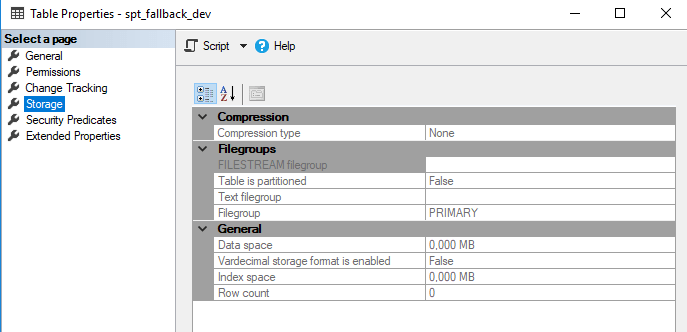
If there are not many objects in the database, you can perform the check directly in the properties of individual tables under the Data space and index space fields. The size of the table is the sum of both values.
More conveniently and quickly, you can obtain statistics on the size of all tables in the database using the following script:
USE [YOUR DATABASE]
SELECT tab.Name AS DB_Table, par.rows AS Table_RowCounts, CAST(ROUND((SUM(alloc.total_pages) / 128.00), 2) AS NUMERIC(36, 2)) AS Table_MBFROM sys.tables tab INNER JOIN sys.indexes ind ON tab.OBJECT_ID = ind.object_id INNER JOIN sys.partitions par ON ind.object_id = par.OBJECT_ID AND ind.index_id = par.index_id INNER JOIN sys.allocation_units alloc ON par.partition_id = alloc.container_idGROUP BY tab.Name, par.rowsORDER BY SUM(alloc.total_pages) DESC;
The result of the script will provide you with a list of all tables in the database, along with the number of rows in each table and the disk space they occupy in MB.