WHERE clause is used to define limit requirements for queries. We are not interested in all records in most cases of queries into tables. Only some subsets of the records based on set criteria are of our interest.
Order of WHERE Clause in SQL Script
- SELECT
- FROM
- WHERE
- GROUP BY
- HAVING
- ORDER BY
Syntax
SELECT [Column 1], [Column 2]
FROM Tabule
WHERE Column <Operator> value;
SQL Operators in WHERE clause
We will take a look at all SQL operators in a separate chapter. Below you can see the list of simple comparison operators which we work with whenever we need to filter data.
- = Equals to
- <> Does not equal to
- < Is lower than
- <= Is lower than or equal to
- > Is higher
- >= Is higher or equal to
Example of WHERE Clause Usage with BETWEEN operator and >= <= operators
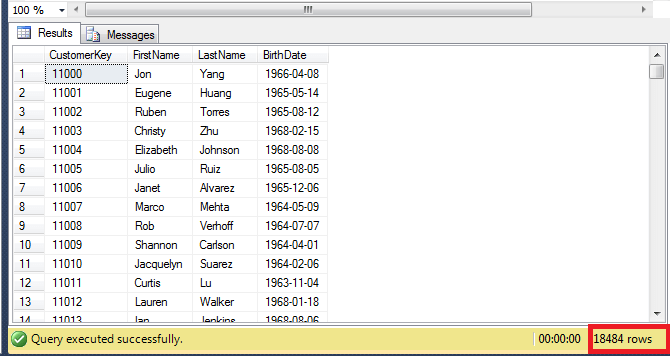
The table which we will use is shown below. It consists of 18484 records.
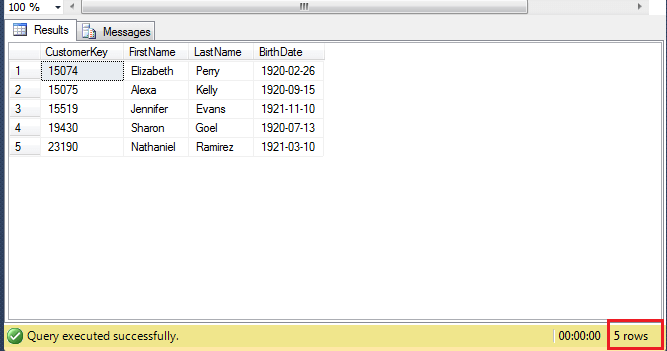
We use clause to filter all customers whose birthday is between 1920-01-01 a 1921-12-31 including. We have two options and the results will be the same.
(i) The first option is to use BETWEEN operator. Marginal dates are included in the requirement.
--Option 1
SELECT [CustomerKey]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[BirthDate]
FROM [AdventureWorksDW2012].[dbo].[DimCustomer]
WHERE BirthDate BETWEEN '1920-01-01' AND '1921-12-31';
(ii) second option is to use operators <= and >= operators
--Option 2
SELECT [CustomerKey]
,[FirstName]
,[LastName]
,[BirthDate]
FROM [AdventureWorksDW2012].[dbo].[DimCustomer]
WHERE BirthDate >= '1920-01-01' AND BirthDate<= '1921-12-31';
The result is 5 records of customers born between 1.1.1920 and 31.12.1921.
For more information, see the official Microsoft documentation