Table Indexes are a fundamental pillar of optimizing SQL queries in a database. They significantly speed up read operations. Unfortunately, over time, indexes get fragmented, and the order of indexes deteriorates. Index fragmentation occurs because records are gradually inserted or deleted from a table, and indexes are not optimized afterward. This means that individual index pages have a lot of free space, and when querying the table, we need to scan more pages than we would if the fragmentation were in order.
Microsoft’s Recommendations for Index Fragmentation
For index maintenance, Microsoft recommends these fragmentation percentages:
- If it is between 5 and 30%, you should reorganize the index (REOGRANIZE).
- If it is greater than 30%, then index rebuilding (REBUILD) is performed.
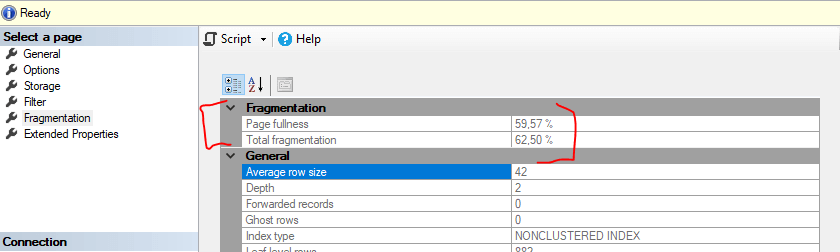
How to Check SQL Index Fragmentation
Fragmentation can be determined in 2 ways:
- Through the properties of a specific index or, even better,
- Using a script (see below).
Index Fragmentation through a Script
Below is a script to find fragmented indexes, i.e., indexes with fragmentation greater than 5%. You need to run the script on the database where you want to check for fragmentation. The SQL query also contains recommendations on what to do with the index (REORGANIZE vs. REBUILD).
SELECT sch.name AS DB_Schema, obj.name AS DB_Table, ind.name AS DB_Index, stat.avg_fragmentation_in_percent AS INDEX_Fragmentation, CASE WHEN avg_fragmentation_in_percent between 5 and 30 THEN 'REORGANIZE' WHEN avg_fragmentation_in_percent >30 THEN 'REBUILD' END AS OperationToMaintenanceFROM sys.objects obj LEFT JOIN sys.schemas sch ON obj.schema_id= sch.schema_id LEFT JOIN sys.indexes ind ON obj.object_id=ind.object_id LEFT JOIN sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats (db_id(), NULL, NULL, NULL, 'LIMITED') AS stat ON ind.object_id=stat.object_id AND ind.index_id=stat.index_idWHERE obj.type='U' AND ind.index_id > 0 AND avg_fragmentation_in_percent>5
Index Maintenance – SQL Syntax
- Index Reorganization:
ALTER INDEX <index_name> ON <table_name> REORGANIZE; - Index Rebuilding:
ALTER INDEX <index_name> ON <table_name> REBUILD;
In the next article, I will show how to automatically repair indexes through an SQL script. You can find the article here – Automatic Index fix.